What is retention? You see this question across industries, and the answer shapes how you measure success. Retention means keeping customers, employees, or learners over time. You track retention to understand loyalty, satisfaction, and value. Look at how different sources define what is retention:
| Source | Definition |
|---|---|
| LiveX | Retention is a measure of a business's ability to maintain its existing customers, reflecting how well a company delivers value and fosters loyalty. |
| Zintego | Customer retention refers to the ability of a company to keep its customers over a defined period, measuring success in maintaining repeat business and building long-term relationships. |
| Darkroom Agency | Retention emphasizes the ability to hold onto customers or employees over time, crucial for ongoing success and stability. |
You rely on retention to measure performance. High retention rates show customers find value and stay loyal. In business, education, contracts, and operations, you see retention as a key metric. Employee turnover rates, for example, impact costs and morale. What is retention in your work? Think about how customer retention, employee retention, and contract retention affect your outcomes.
You see retention as the ability to keep something valuable over time. In every field, retention means holding on to people, knowledge, or resources that matter to your goals. You measure retention to understand how well you maintain relationships, preserve information, or protect assets. When you focus on retention, you look at how many customers return, how many employees stay, or how much knowledge remains in your organization. Retention helps you see if your strategies work and if your efforts lead to long-term success.
Retention involves several core elements that help you organize and manage what you want to keep. The table below shows the main components that define retention in a universal context:
| Core Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Retention Schedule | An organized hierarchy of series, categories, and record folders that cluster retained content. |
| Series | An organizational construct that groups categories into functional groups, often static in nature. |
| Retention Category | A set of security settings and disposition instructions that groups items with the same dispositions. |
| Record Folder | A collection of similar content items, organized into groups following the associated retention category. |
| Disposition | The actions taken on items, including deletion and transfer to storage. |
| Disposition Instruction | Rules defining how content is handled and when actions should be taken. |
| Period | The time segment that must pass before a review or disposition action can occur. |
| Trigger | An event that must occur before a disposition instruction is processed. |
| Classification | Specifies the security level of an item, aiding in the safeguarding of sensitive information. |
| Freezing | Inhibits disposition processing for compliance with legal or audit requirements. |
You use these elements to build a strong retention system. This system helps you track what you keep, why you keep it, and how you protect it. You can apply these principles to customer data, employee records, or even digital content.
You encounter different types of retention in your daily work. Each type focuses on keeping something important for your organization or personal goals. Here are the main types you should know:
You see real-world examples of retention every day. Companies use creative strategies to improve customer retention and build lasting relationships. For example:
You can apply these lessons to your own work. When you focus on retention, you create value for your customers, employees, and organization. You build trust, encourage repeat business, and support long-term growth.
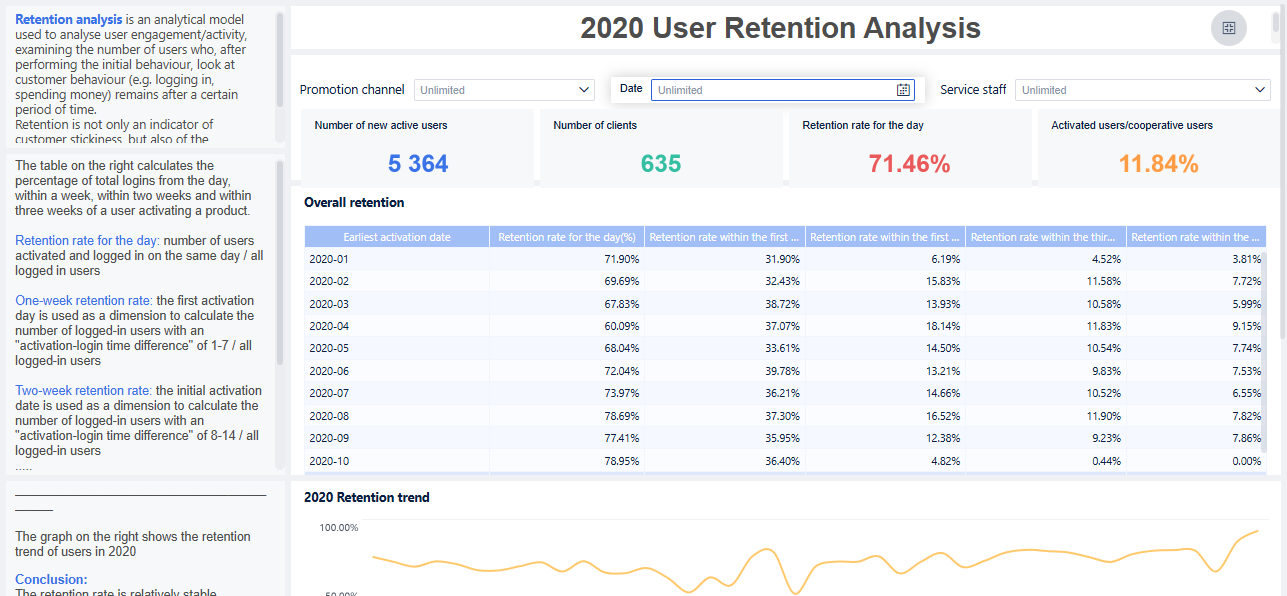
Retention plays a vital role in your organization’s success. You see its impact in business, education, contracts, and operations. When you focus on retention, you build strong relationships with customers, employees, and partners. You create long-term relationships that drive growth and stability.
You notice the importance of retention in several ways. In business, customer retention helps you maintain revenue and reduce costs. You spend less to keep existing customers than to attract new ones. High retention rates show that customers trust your brand and value your products. In education, retention means students remember what they learn and apply it in real life. In contracts, retention ensures you meet legal requirements and protect your interests. In operations, retention keeps your processes running smoothly and maintains quality.
The table below highlights why retention is critical across different fields:
| Metric | Importance |
|---|---|
| Customer Retention Rate (CRR) | Indicates the percentage of customers retained over a specific period, reflecting loyalty. |
| Repeat Purchase Rate (RPR) | Measures how often customers return to make additional purchases, indicating satisfaction. |
| Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) | Estimates the total revenue a business can expect from a customer over their lifetime, guiding investment in retention strategies. |
| Net Promoter Score (NPS) | Gauges customer satisfaction and loyalty by asking how likely customers are to recommend the business. |
| Churn Rate | Represents the percentage of customers who stop using a service, highlighting retention challenges. |
You see that 73% of consumers abandon a brand after one bad customer service experience. This fact shows the need for effective retention strategies. You also learn that it costs four to five times more to acquire a new customer than to retain an existing one. These numbers prove the importance of retention for your bottom line.
When you achieve high retention rates, you build loyalty and trust. You strengthen relationships with customers and employees. You create a stable environment that supports growth. Effective retention helps you avoid the costs and disruptions caused by turnover or lost customers. You see the value in investing in retention strategies that support long-term relationships.
Measuring retention gives you insight into your organization’s performance. You use retention metrics to track how well you keep customers, employees, or resources. You rely on these metrics to guide your decisions and improve your strategies.
You use several methods to measure retention. For daily-use products, you track return on retention. For products with varied usage patterns, you use return on or after retention. You can also customize your approach with return on (custom) retention to fit your business goals.
Common retention metrics include:
Measuring retention helps you identify strengths and weaknesses. You see which strategies work and where you need improvement. High retention rates mean your customers and employees stay loyal. Low retention rates signal problems that need attention.
High employee turnover can be detrimental to an organization's overall success. The costs of recruiting, hiring, and training new employees can be significant. Not only does this drain financial resources, but it also diverts the focus of management from core business operations. High turnover rates can have a negative impact on employee morale and engagement, leading to decreased motivation, lower productivity levels, and higher turnover rates.
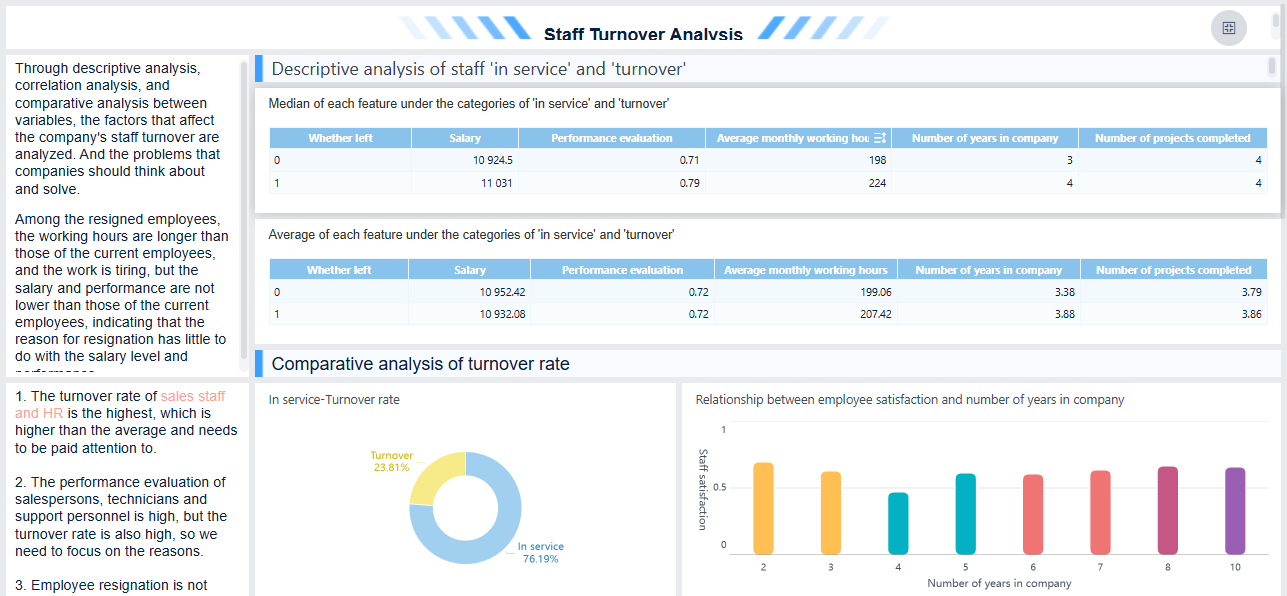
You face substantial costs when you lose employees or customers. Organizations may have to invest an amount equivalent to six to nine months of an employee’s salary to locate and educate a replacement. You see similar costs when you lose customers and must spend more to attract new ones.
Retention rates affect every part of your organization. High retention rates lead to strong relationships, loyalty, and long-term relationships. You build a foundation for growth and stability. Low retention rates create challenges and increase costs. Measuring retention helps you stay on track and achieve your goals.

Customer retention refers to your ability to keep customers returning and making purchases over time. You use customer retention as a key metric for customer engagement and loyalty. High retention rates show that your customers find value in your products and services. When you focus on retention, you reduce customer turnover and increase customer satisfaction. You also improve customer lifetime value, which measures the total revenue you can expect from a customer throughout their relationship with your business.
You see that customer retention is significant for business growth. It costs five times more to attract a new customer than to keep an existing one. High retention rates lead to increased revenue and profitability. When you retain customers, you build customer loyalty and strengthen your brand. Satisfied customers are more likely to make repeat purchases and recommend your business to others. Low retention can result in higher churn and decreased revenue.
FineBI helps you track and improve customer retention by providing powerful analytics tools. You can use FineBI dashboards to monitor customer retention rate, customer satisfaction, and customer lifetime value in real time. FineBI enables you to segment customers based on behavior, purchase history, and engagement. This segmentation allows you to tailor marketing efforts and personalize communication. You can analyze user behavior signals to optimize your retention strategies and increase customer satisfaction. FineBI also supports recommendation engines that help you identify cross-selling and upselling opportunities, similar to leading e-commerce platforms.
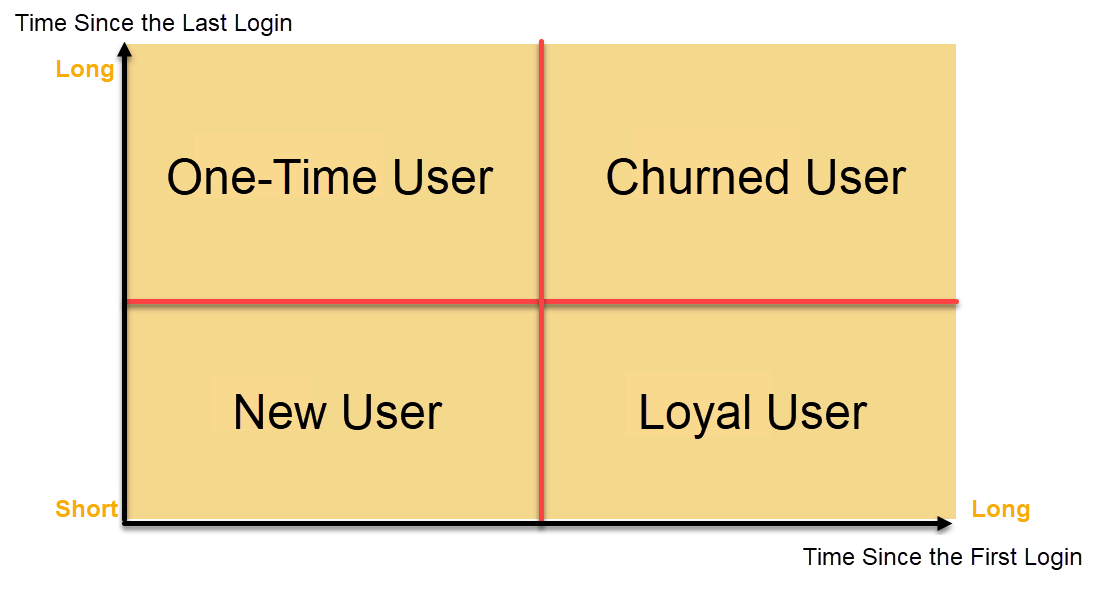
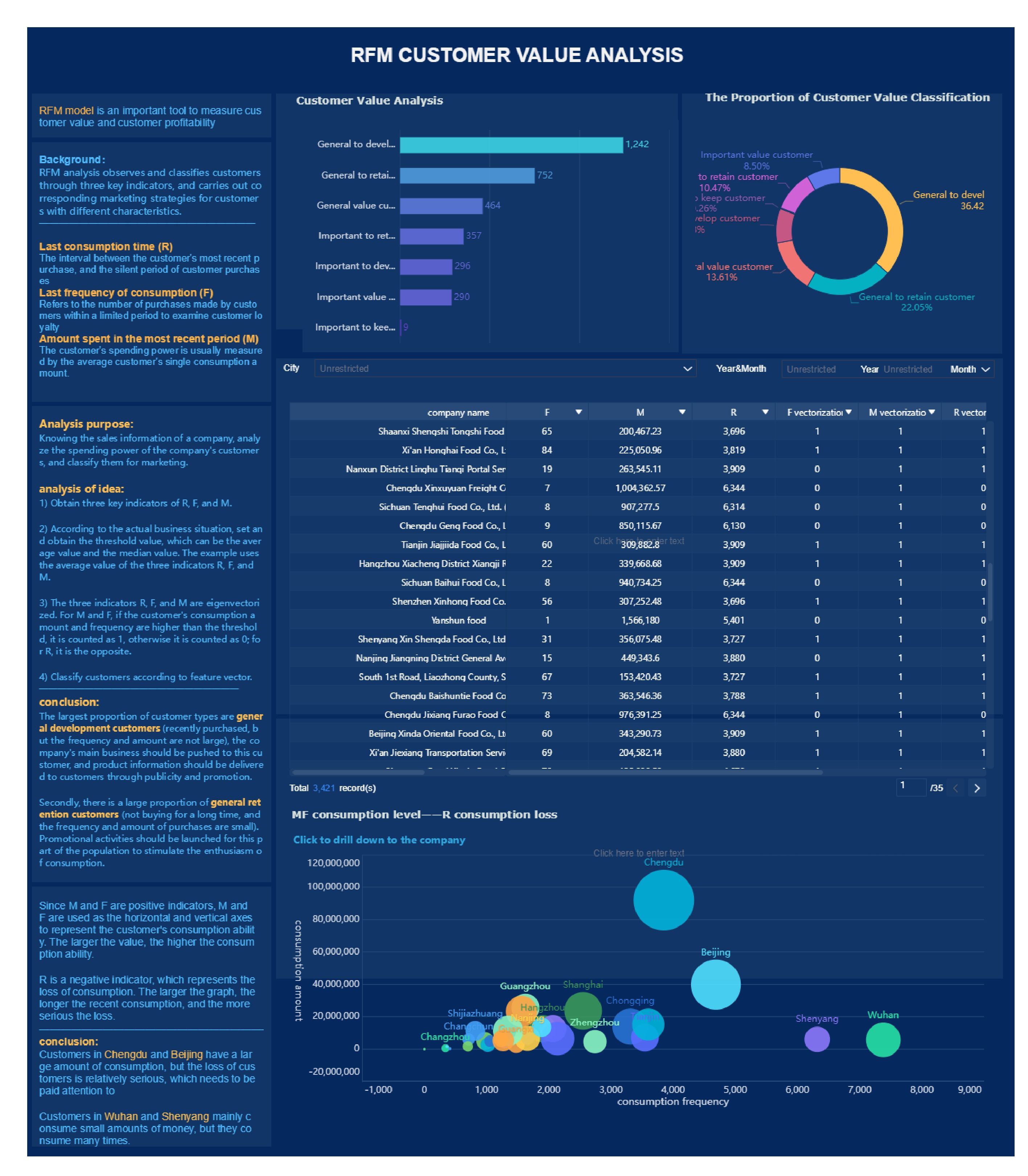
Retailers benefit from FineBI’s membership management solution. For example, you can use RFM modeling to segment customers by recency, frequency, and monetary value. This approach helps you target high-value customers and improve customer lifetime value. UnionPay Data Services used FineBI to unify data, identify key customer segments, and boost engagement. Their system operation efficiency increased, and customer value identification accuracy reached 90%. These results show how data-driven retention strategies can transform your business.
You can apply several actionable retention strategies to enhance customer satisfaction and increase customer lifetime value:
Personalization can reduce customer acquisition costs by up to 50%. It can also increase revenues by 5% to 15% and improve marketing ROI by 10% to 30%. When you focus on building customer loyalty and maximizing customer lifetime value, you create a strong foundation for long-term business success.

You encounter learning retention every time you try to remember what you studied last week. Learning retention measures how much information you can recall accurately over time. If you score high on a test right after a lesson but much lower a week later, your retention is low. This gap shows the importance of moving knowledge from short-term to long-term memory. When you focus on teaching for retention, you help students build strong memory skills that support successful learning.
Enjoyable learning experiences play a big role in retention. When you find lessons engaging, your brain releases dopamine, which boosts attention and memory. You remember more when you enjoy the process. Students who like learning often stay curious and keep exploring topics outside the classroom. To improve retention, you can use strategies like spaced learning, retrieval practice, and microlearning. These methods help transfer knowledge into long-term memory and make lessons stick.
| Method/Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Immediate vs. delayed assessments | Short quizzes test initial understanding; delayed tests show long-term retention. |
| Spaced Learning | Break lessons into intervals to reinforce memory over time. |
| Retrieval Practice | Regular quizzes strengthen memory and retention. |
| Microlearning | Bite-sized lessons reduce overload and increase recall. |
| Feedback Loops | Immediate feedback helps correct mistakes and improve retention. |
You see contract retention in many industries, especially construction and employment. Contract retention means holding back a portion of payment to ensure all obligations are met and quality standards are achieved. Retention clauses in contracts define how much money is withheld, when it will be released, and under what conditions. These clauses protect both parties by making sure work is completed properly and any defects are fixed.
For project owners, contract retention ensures quality work and provides funds to address problems. For contractors, it encourages accountability and performance, though it may limit cash flow. Key elements of retention clauses include the retention percentage, release terms, defect liability period, and retention cap. In construction, you often see a retention amount of 5-10%, with clear rules for release and dispute resolution. In employment contracts, retention can involve bonuses, terms of service, and confidentiality clauses to help retain talent and minimize turnover.
| Industry | Common Practices |
|---|---|
| Construction | Define retention amount, set release conditions, outline dispute procedures, comply with laws |
| Employment | Offer retention bonuses, set terms of service, include forfeiture and non-compete clauses |
You measure contract retention by tracking compliance with these terms and monitoring the release of retained funds. By using clear retention strategies, you protect your interests and support long-term business relationships with customers, employees, and partners.
You see retention in product management as a measure of how well your products keep customers engaged and satisfied over time. High retention in product management means your customers continue to use your products, which shows a strong relationship between your offerings and their needs. You want to understand why customers stay with your product and what makes them leave. When you focus on retention in product management, you improve customer loyalty and reduce the cost of acquiring new customers.
Process retention focuses on how well your operations keep customers satisfied throughout their journey. You want every step, from order processing to after-sales support, to strengthen the relationship with your customer. FineBI helps you monitor and optimize operational retention by providing real-time insights and flexible analysis tools.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Real-time Monitoring | You gain immediate insights into supply-chain activities, supporting timely decisions. |
| Drill-through | You analyze specific metrics in depth, improving targeted management practices. |
| Filtering | You customize data views, focusing on the information most relevant to retention goals. |
You see real-world improvements in service industries when you apply strong retention in product management and process retention:
You use retention in product management and process retention to create a seamless experience for your customers. When you monitor these areas with tools like FineBI, you strengthen every relationship and support long-term business growth.
Retention delivers value across every field. You see its impact in business, education, contracts, and operations:
You can use analytics tools like FineBI to predict customer churn, segment customers, and respond to feedback in real time.
When you focus on retention, you create a stable environment for customers and employees. You support innovation and long-term success. Start applying retention strategies and data-driven tools to keep your customers engaged and your organization growing.

How to Do Retention Analysis for Business Success
What is Pareto Chart and How Does it Work
How DuPont Analysis Helps You Understand Your Business

The Author
Lewis
Senior Data Analyst at FanRuan
Related Articles

Self-Service Analytics Defined and Why You Need It
Self-service analytics lets you analyze data without IT help, empowering faster, data-driven decisions and boosting agility for your business.
Lewis
Jan 04, 2026

Best Self-Service Tools for Analytics You Should Know
See which self-service tools for analytics let business users access data, build dashboards, and make decisions faster—no IT help needed.
Lewis
Dec 29, 2025

Understanding Predictive Analytics Services in 2026
Predictive analytics services use data and AI to forecast trends, helping businesses make informed decisions, reduce risks, and improve efficiency in 2026.
Lewis
Dec 30, 2025