Imagine having all your data in one place, neatly organized and easy to explore. That’s exactly what an interactive dashboard in Excel offers. It’s a tool that lets you visualize data through charts, tables, and filters, making complex information simple to understand.
Why is this important? Interactive dashboards make data analysis faster and decision-making smarter. Real-time updates let you spot trends and outliers instantly. For example:
| Dashboard Type | Purpose |
| Financial Dashboard | Monitors financial performance using key KPIs for executives and finance teams. |
| Marketing Performance Dashboard | Visualizes marketing metrics to assess progress towards marketing goals. |
| Sales Management Dashboard | Evaluates sales performance by region, outlet, and individual sales representatives. |
| Project Management Dashboard | Tracks project timelines, budgets, and task statuses for efficient management. |
Let's look at some real-world examples:
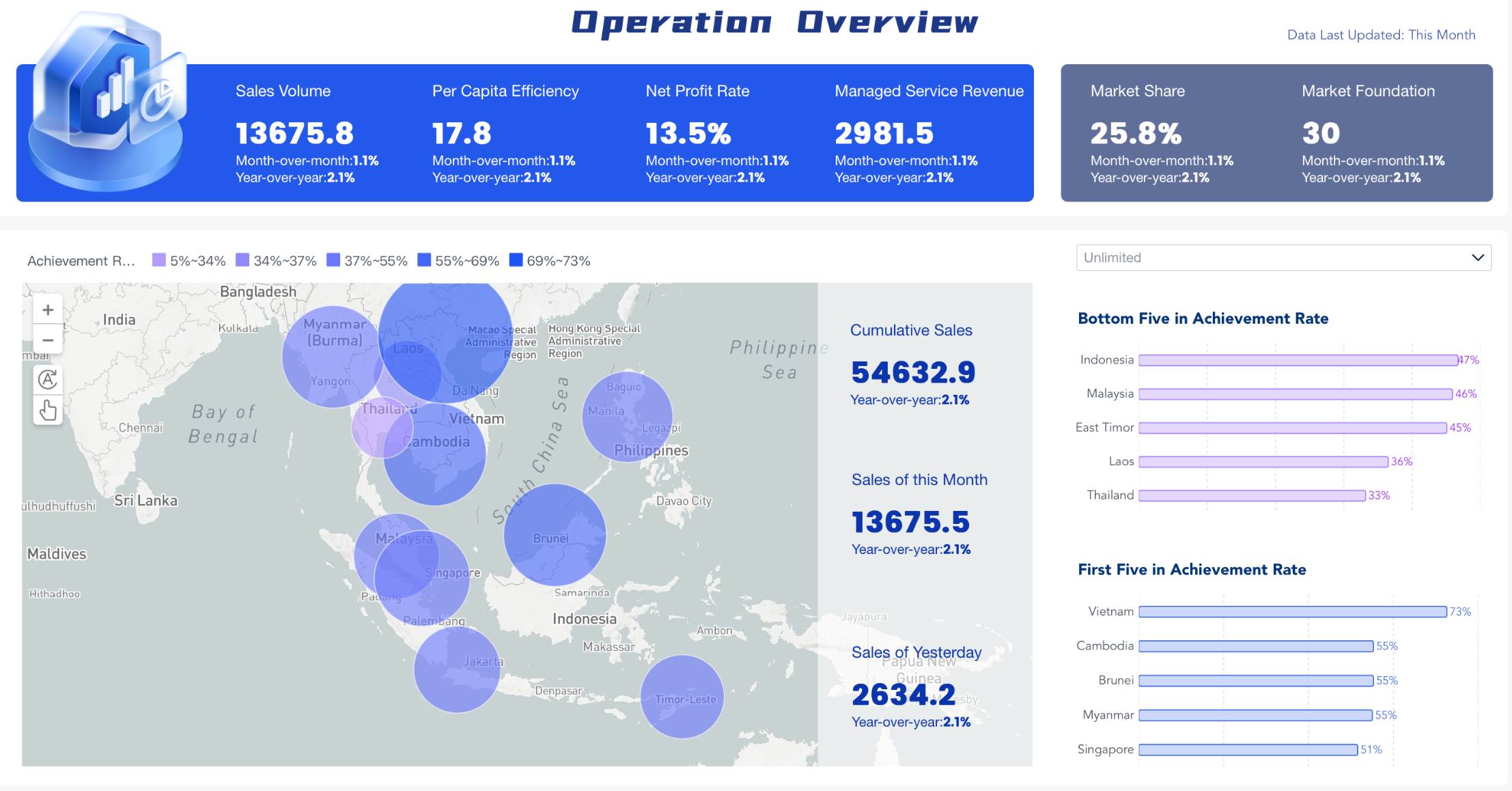
With tools like these, you can respond quickly to changes and make informed decisions. Ready to learn how to create a dashboard in Excel? While Excel is a great starting point, some organizations might also consider specialized business intelligence tools like FineReport from FanRuan, which offers enhanced data visualization capabilities while maintaining a familiar spreadsheet-like interface. However, let's focus on how to create your dashboard in Excel.This comprehensive guide will show you exactly how to create a dashboard in Excel from start to finish.
Creating an interactive dashboard in Excel starts with a solid plan. Without a clear purpose, your dashboard can quickly become cluttered and confusing. Let’s break down the planning process into three simple steps.
Before you dive into Excel, ask yourself: What do you want your dashboard to achieve? Are you tracking sales performance, monitoring financial health, or analyzing marketing campaigns? Defining your objectives helps you focus on the right data and avoid unnecessary distractions. For example, if your goal is to track sales growth, you might prioritize metrics like total revenue, conversion rates, and customer acquisition costs.
Think about your audience too. Executives might need high-level summaries, while analysts may require detailed insights. Knowing who will use the dashboard ensures you include the right information. Once you’ve identified your goals, gather accurate and relevant data. Clean, organized data is the foundation of any successful Excel dashboard. For instance:
An e-commerce company might create a dashboard tracking:
A human resources department could build a dashboard showing:
Your audience plays a huge role in shaping your dashboard. What decisions will they make based on the data? What information do they need to see first? Asking these questions helps you design a dashboard that’s both useful and user-friendly. For instance, you might include graphs for executives to visualize trends or detailed tables for analysts to dig deeper into the numbers.
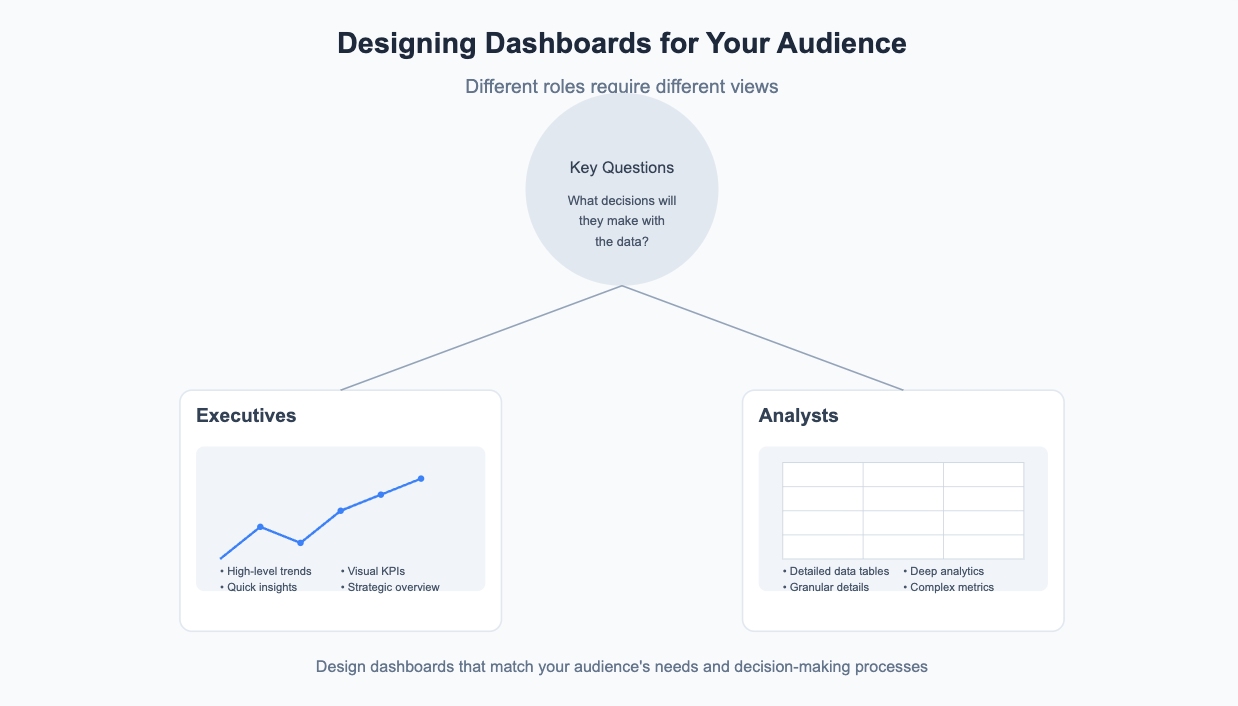
You can also explore other dashboards your audience has used and liked. This gives you a sense of what works and what doesn’t. Keep in mind that too much information can overwhelm users. Stick to the essentials and make navigation simple.
A well-organized layout makes your dashboard easy to read and understand. Start by sketching a rough design. Place the most important metrics at the top or center, where they’re immediately visible. Use sections to group related data logically. For example, you could dedicate one area to financial KPIs and another to sales performance.
Choosing the right metrics is equally important. Focus on key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with your goals. For a financial dashboard, you might include metrics like net profit, cash flow, and operating income. For a sales dashboard, consider metrics like closed deals, sales growth, and customer lifetime value. Use visuals like charts and graphs to make the data more engaging and easier to interpret.
By following these steps, you’ll set a strong foundation to create an interactive dashboard in Excel that’s both functional and visually appealing. For more complex enterprise scenarios, tools like FineDatalink can complement Excel by providing robust data integration capabilities, but for most business needs, Excel's built-in features are sufficient. Let's continue exploring how to create a dashboard in Excel by looking at data import.
Before you can create an interactive dashboard in Excel, you need to get your data ready. This step is all about collecting, importing, and organizing your data so it’s easy to work with. Let’s break it down.
Start by gathering the data you’ll use in your dashboard. Think about your objectives. Are you tracking sales, monitoring KPIs, or analyzing trends? Knowing your goal helps you focus on the right data. For example, if you’re building a sales dashboard, you might collect data on revenue, customer acquisition, and sales growth.
Once you have your data, make sure it’s clean and accurate. Remove duplicates, fix errors, and ensure consistency in formatting. Organized data saves you time and prevents mistakes later. Also, consider where your data comes from. Is it in a spreadsheet, a database, or an external source? Reliable data sources ensure your dashboard stays accurate and up-to-date.
Now it’s time to bring your data into Excel. If your data is already in a spreadsheet, you’re good to go. But if it’s stored elsewhere, like in a database or an online tool, you’ll need to import it. Excel makes this easy with its built-in tools.
For example, you can use the “Get & Transform” feature to connect to external data sources. This tool lets you pull in data from websites, databases, or even other Excel files. Enterprise users might also leverage FineDatalink for more sophisticated data integration needs, especially when dealing with multiple database types and real-time data synchronization. However, for standard reporting needs, Excel's native features work well.Once imported, check that everything looks correct. If something seems off, go back and fix it before moving forward.
Tables are your best friend when organizing data in Excel. They make it easier to manage and analyze your information. To create a table, select your data and press Ctrl + T. This adds filters and formatting automatically, making your data more readable.
Tables also make your dashboard dynamic. When you add new data, the table updates automatically. This means your charts and visuals will refresh without extra work. Plus, tables work well with features like slicers and pivot tables, which you’ll use later to create an interactive dashboard.
By following these steps, you’ll have a solid foundation to create an Excel dashboard that’s both functional and easy to update. With your data imported and organized, you’re ready to move on to the fun part—visualizing your data!
Before you dive into creating visuals for your interactive dashboard in Excel, you need to prepare your data. Clean and well-organized data ensures your dashboard works smoothly and delivers accurate insights. Let’s go through the key steps to get your data ready.
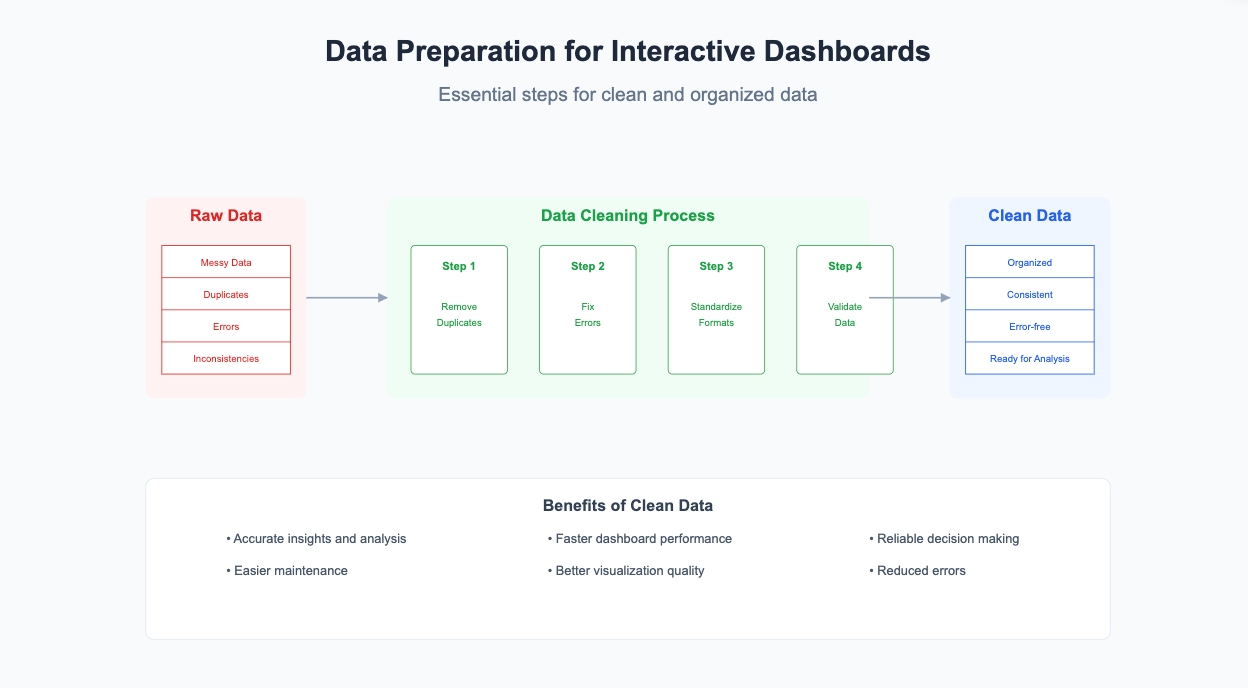
Duplicate entries and errors can mess up your analysis. Removing them is essential for a reliable dashboard. Excel offers simple tools to help you clean your data:
These steps ensure your data is error-free and ready for analysis. This preparation is crucial when learning how to create a dashboard in Excel.
Consistent formatting makes your data easier to read and analyze. It also builds trust in your dashboard. For example, ensure dates follow the same format, numbers have the correct decimal places, and text entries are uniform.
Here’s why formatting matters:
| Benefit | Description |
| Promotes trust | Ensures that core metrics driving growth are reliable and trustworthy. |
| Saves time and resources | Reduces the time spent on generating reports and minimizes bottlenecks caused by formatting issues. |
| Increases visibility | Enhances understanding of data quality, aiding in informed decision-making across the organization. |
| Creates accountability | Allows managers to track key performance metrics and ensure standards are met. |
Taking the time to format your data properly will save you headaches later when you create an excel dashboard.
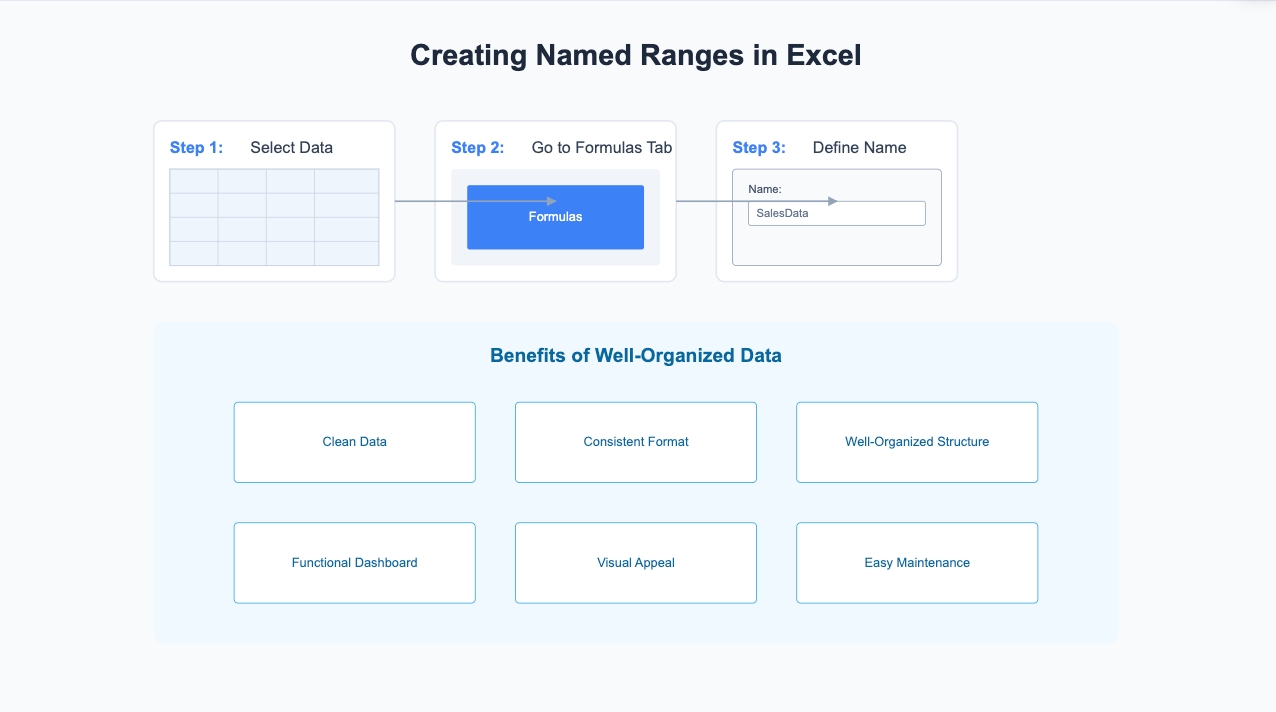
Named ranges make managing your data easier, especially when you create an interactive dashboard. Instead of referring to cells like A1:A100, you can assign a name like SalesData. This makes formulas and references clearer and reduces errors.
Dynamic named ranges are even better. They automatically adjust as you add or remove data, ensuring your dashboard stays up-to-date. For example, if you’re tracking monthly sales, a dynamic range will include new months without requiring manual updates. This feature is perfect for dashboards that rely on constantly changing data.
To create a named range, select your data, go to the Formulas tab, and click Define Name. Give your range a meaningful name, and you’re all set!
By following these steps, you’ll have clean, consistent, and well-organized data. This solid foundation will make it easier to create a dashboard in Excel that’s both functional and visually appealing.
Now that your data is clean and organized, it’s time to bring it to life with visuals. Charts, pivot tables, and conditional formatting are the building blocks of an engaging and insightful dashboard. Let’s explore how you can use these tools to create an interactive dashboard in Excel.
Charts are the heart of any dashboard. When learning how to create a dashboard in Excel, choosing the right charts is essential. They transform raw numbers into visuals that are easy to understand. But not all charts are created equal. Choosing the right one depends on the story you want to tell.
Here’s a quick guide to help you decide:
| Chart Type | Description | Use Case Example |
| Bar and Column | Present data clearly and visually. | Compare sales across regions or products. |
| Line | Spot trends over time by connecting data points. | Track monthly revenue or expenses. |
| Pie | Show how categories contribute to a total. | Illustrate budget allocation across departments. |
| Combo | Combine multiple chart types for deeper insights. | Compare revenue and profit margins simultaneously. |
| Waterfall | Visualize cumulative effects of sequential values. | Analyze profit margins or cost breakdowns. |
For example, if you’re tracking sales growth, a line chart can highlight trends over time. On the other hand, a pie chart works well for showing how different products contribute to total revenue. Experiment with different types to find what works best for your dashboard.
Pivot tables are a game-changer for summarizing large datasets. They let you group, filter, and analyze data without complex formulas. With just a few clicks, you can create summaries that highlight key insights.
For instance, you can use a pivot table to break down sales by region, product, or salesperson. This makes it easier to spot patterns and identify areas for improvement. To get started, select your data, go to the Insert tab, and choose Pivot Table. From there, drag and drop fields to organize your data however you like. Pivot tables are flexible and perfect for creating a dynamic excel dashboard.

Conditional formatting adds a layer of interactivity to your dashboard. It highlights important data points automatically, so you can focus on what matters most.
Here are some ways you can use it:
For example, in a sales report, you could color cells red if sales fall below a target or green if they exceed it. This makes it easy to spot underperforming areas at a glance. Conditional formatting turns your dashboard into a powerful tool for quick decision-making.
By combining charts, pivot tables, and conditional formatting, you can create an interactive dashboard that’s both functional and visually appealing. These tools make it easier to analyze data and share insights effectively.
Interactive features make your dashboard more engaging and user-friendly. Understanding how to create a dashboard in Excel means mastering these interactive elements. They allow users to explore data, filter information, and interact with visuals effortlessly. To help you master these interactive features, we'll provide step-by-step instructions and practical examples for each method.
Slicers are a fantastic way to make your dashboard dynamic and interactive. Detailed steps to create and implement slicers:
Pro tip: Create separate slicers for different dimensions (e.g., products, regions, time periods) to allow multi-dimensional analysis.
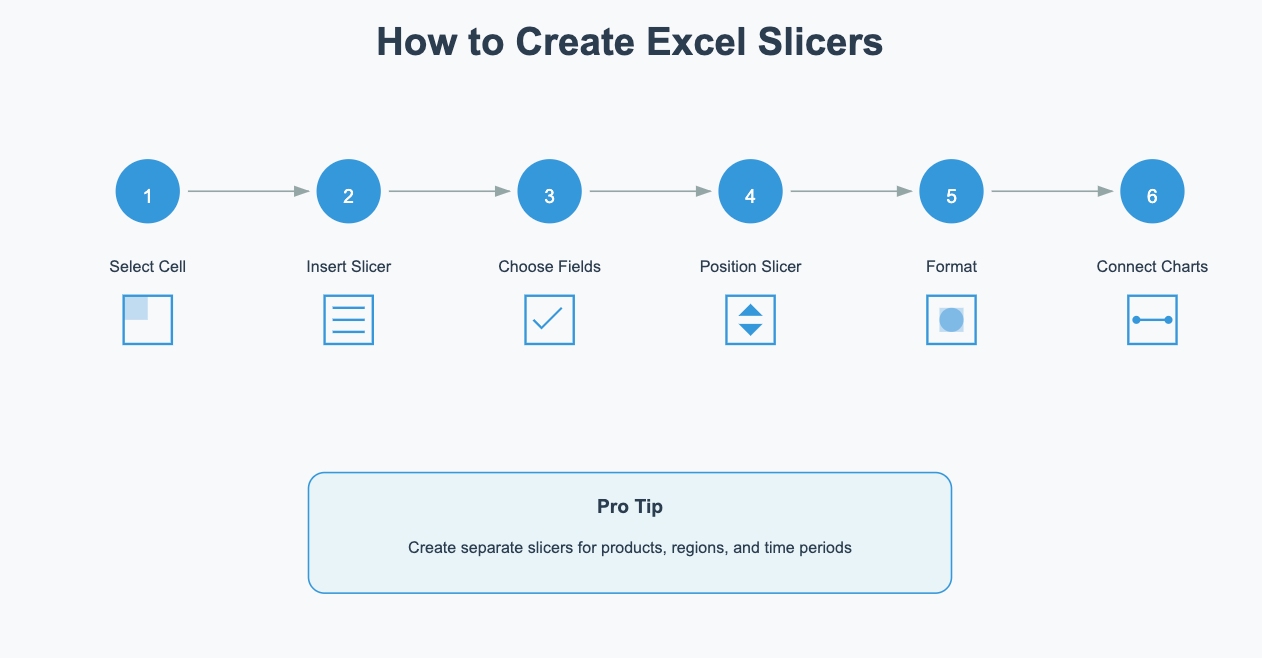
They act as visual filters, letting users select specific data categories and instantly see the impact on charts and tables.
For example, if your dashboard tracks sales, you can add slicers for regions or product categories. Users can click on a region to see its sales performance without affecting other parts of the dashboard. This feature encourages exploration and helps users discover insights independently.
Drop-down menus are another great way to create an interactive dashboard.
They let users select options that automatically update charts and tables. Here’s how you can set one up:
=Db1_Country.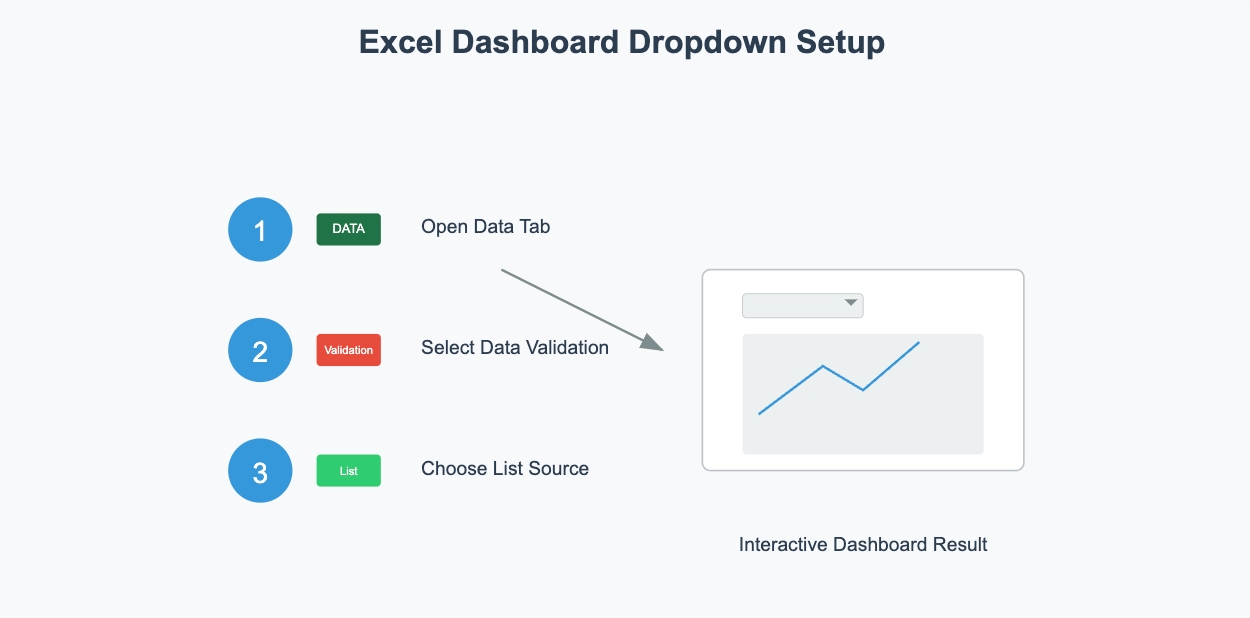
Drop-down menus are perfect for dashboards that need user input. For instance, you can use them to let users choose a time period, such as monthly or quarterly data. This makes your dashboard more flexible and engaging.
Buttons add another layer of interactivity to your Excel dashboard. They can help users navigate between sheets or trigger specific actions, like refreshing data or resetting filters. You can create buttons using Excel’s Form Controls. Assign macros to these buttons to automate tasks and make your dashboard more dynamic.
For example, you could add a button labeled “Reset Filters” to clear all slicers and drop-down selections. This makes it easier for users to start fresh without manually undoing changes. Buttons not only enhance usability but also give your dashboard a polished, professional look.
By incorporating slicers, drop-down menus, and buttons, you can create an interactive dashboard that’s both functional and engaging. You can peruse this interactive feature troubleshooting guide.
1. Slicer not updating charts
- Check report connections
- Verify data source links
2. Drop-down list not showing all items
- Check source range
- Verify dynamic range names
3. Buttons not responding
- Enable macros
- Check VBA references
Performance Optimization Tips:
1. Limit number of slicers to prevent slowdown
2. Use efficient formulas for drop-down dependencies
3. Optimize macro code for faster execution
4. Cache data for frequently used filters
These features transform your Excel dashboard into a powerful tool for exploring and analyzing data.

Once you’ve added interactivity to your dashboard, it’s time to focus on design. This final stage of how to create a dashboard in Excel will polish your work to professional standards. A polished dashboard not only looks professional but also makes data easier to understand. Let’s explore how you can refine your dashboard with consistent colors, clear labels, and usability testing.
Colors and fonts play a huge role in making your dashboard visually appealing and easy to read. Here are some best practices to follow:
When it comes to colors, less is more. A simple color scheme with four or fewer colors works best. Consider these tips:
Consistency in colors and fonts ensures your dashboard feels cohesive and professional.
Titles, labels, and tooltips are essential for clarity. They guide users and help them understand the data at a glance. Here’s why they matter:
| Benefit | Explanation |
| Clarity | Titles and labels provide context, making it clear what each chart or table represents. |
| Reduced Confusion | Users can interpret visuals more easily, reducing the chance of misinterpretation. |
| Enhanced Value | Descriptive labels and tooltips add depth, improving the overall user experience. |
For example, add a title like “Monthly Sales Performance” to a line chart. Use labels to show exact values on data points. Tooltips can provide additional details when users hover over a chart. These small touches make your dashboard more user-friendly.
Before sharing your dashboard, test it thoroughly. Start by checking all links, calculations, and visuals. Compare the results to your original data to ensure accuracy.
Next, share the dashboard with stakeholders and ask for feedback. They might spot areas for improvement that you missed. Use their input to refine your design and functionality.
Testing and adjustments ensure your dashboard works smoothly and meets user needs. A well-tested dashboard builds trust and delivers reliable insights.
By focusing on design and usability, you’ll create a dashboard in excel that’s not only functional but also a pleasure to use.
How to create a dashboard in Excel might seem overwhelming, but breaking it into steps makes it manageable. Here’s a quick recap:
Excel offers several advantages for building dashboards.
| Benefit | Description |
| Familiarity | Many users already know Excel, so there’s no steep learning curve. |
| Flexibility | It provides tools for data analysis and visualization. |
| Cost-Efficiency | It’s part of Microsoft Office, so no extra software costs are needed. |
| Integration | Works seamlessly with other Microsoft Office applications. |
However, Excel has its limits. It struggles with large datasets and lacks real-time updates. Collaboration can also be tricky. For organizations facing these limitations, solutions like FineReport and FineVis offer enhanced capabilities for handling large-scale data visualization and real-time updates while maintaining a familiar interface for Excel users. These tools can serve as a natural progression when your reporting needs outgrow Excel's capabilities. If you need advanced features, consider tools like Power BI or Tableau. These platforms handle big data better and offer more customization options.
By following these steps and understanding Excel’s strengths and weaknesses, you can create a dashboard that’s both functional and visually appealing.
Click the banner below to experience FineReport for free and empower your enterprise to convert data into productivity!

How to Quickly Build a Core App Dashboard
Store Performance Dashboard: Your Retail Command Center
Dynamic Dashboard: A Game Changer for Data Analysis
Master the Square Dashboard in Easy Steps
How to Design a Client Dashboard That Delivers Results
Draft Dashboard Review - Is It the Ultimate DFS Tool?
Mastering the Twitch Dashboard for Streamer Success
Using the Blooket Dashboard to Boost Student Engagement
Mastering the Unity Cloud Dashboard for Effective Use
How to Access the Clover Dashboard Easily
How to Access the Chrysler Employee Portal Easily
Covers Dashboard: Find Your Perfect Match

The Author
Lewis
Senior Data Analyst at FanRuan
Related Articles

Top 10 OKR Dashboard Examples to Boost Your Goals
See the top 10 OKR dashboard examples for 2026 to track goals, align teams, and boost performance with real-time progress and integrations.
LewisEric
Jan 13, 2026

What Is an Operational Dashboard and How Does It Work
An operational dashboard provides real-time monitoring of key metrics, helping you track business activities, spot issues, and optimize operations instantly.
Lewis
Jan 12, 2026

Restaurant Dashboard Tricks for Smoother Daily Operations
Use a restaurant dashboard to streamline daily operations, monitor sales, manage staff, and boost efficiency with real-time data and automated alerts.
Lewis
Jan 12, 2026